Alternatives and Competitors
•
Feb 19, 2026
Zapier Alternatives in 2026: 7 Better and More Scalable Replacements
Looking for a better alternative to Zapier? Compare the 7 best Zapier competitors in 2026, ranked by automation depth, AI-native capability, and long-term scalability.
Written By :

Divit Bhat
Zapier didn’t just popularize automation. It defined it.
For over a decade, “set up a Zap” became shorthand for connecting apps. If you needed a trigger-action workflow, Zapier was the answer. It earned that position.
But the automation landscape it was built for no longer exists.
According to the latest publication from Meticulous Research, the global workflow automation market is projected to reach $77.8 billion by 2035, at a CAGR of 21.3% from 2023 to 2030., driven largely by AI-native systems and infrastructure-level orchestration rather than simple app-to-app triggers. Automation is no longer a convenience layer. It’s becoming an operational core.
In 2026, automation isn’t about passing data between tools. It’s about orchestrating AI agents, handling stateful logic, managing infrastructure-level workflows, and embedding execution directly into products. The trigger-action model that once felt revolutionary now shows structural limits when applied to modern systems.
The shift isn’t subtle.
SaaS stacks are larger. AI is no longer experimental. Workflows are no longer linear. And task-based pricing models that worked at 1,000 events per month become operational bottlenecks at 100,000.
This guide doesn’t compare surface-level features.
It ranks platforms by automation depth, execution model, and long-term scalability. It breaks down why some tools are still operating at workflow level, while others are evolving into infrastructure. And it explains why AI-native systems are redefining what automation even means.
Zapier still works for simple, linear workflows. But if you’re building systems instead of tasks, the conversation has already moved on.
Let’s examine what replaces it.
Quick Comparison Snapshot
Below is a high-level comparison of the most relevant Zapier alternatives in 2026, ranked by automation depth rather than popularity.
Platform | Best For | Automation Depth | Pricing Model | AI-Native | Ideal Use Case |
Emergent | AI-native infrastructure & product automation | Level 4 — Infrastructure | Infrastructure-based execution | Yes, native | Building AI-powered systems and scalable backend automation |
n8n | Developer-controlled workflows | Level 2.5 — Advanced workflows | Execution-based | Limited | API-heavy logic and custom integrations |
Make | Visual multi-step workflows | Level 2 — Logic automation | Operation-based | Limited | Complex branching with visual builder |
Workato | Enterprise automation | Level 3 — Enterprise orchestration | Enterprise-tier pricing | Partial | Large organizations integrating internal systems |
Activepieces | Open-source workflows | Level 2 — Modular automation | Usage-based / self-hosted | Limited | Teams wanting open-source flexibility |
Tray.io | Enterprise-grade workflow orchestration | Level 3 — Enterprise automation | Enterprise-tier pricing | Partial | Scalable enterprise integration layers |
Pabbly Connect | Budget task automation | Level 2 — Trigger-action | Subscription-based | No | Simple, low-cost automations |
How to Read This Table?
Most comparison guides rank tools by feature count or pricing.
This one ranks them by automation depth, meaning how far you can scale before hitting architectural ceilings.
If you’re automating a few tasks, Level 2 tools work.
If you’re orchestrating AI agents, embedding automation into products, or scaling execution-heavy systems, only Level 4 platforms truly qualify.
We’ll break down exactly what that means next.
What Is the Best Zapier Alternative in 2026?
The best Zapier alternative depends on what level of automation you actually need.
If you’re running simple, linear trigger-action workflows at low volume, Zapier still works. It remains one of the easiest tools for basic app-to-app automation.
If you need deeper logic, API-level control, or self-hosted flexibility, platforms like n8n offer more architectural control than traditional Zapier-style tools.
If you’re operating at enterprise scale and integrating internal systems across departments, tools like Workato or Tray.io provide stronger governance and compliance layers.
But if you’re building AI-native systems, orchestrating stateful workflows, embedding automation into products, or scaling beyond task-based pricing constraints, infrastructure-level platforms like Emergent represent a fundamentally different category.
The real distinction isn’t features - It’s automation maturity.Some tools help you automate tasks.Others let you automate systems.
The best choice depends on which level you’re operating at.
The Automation Industry Has Outgrown Zapier’s Original Model
Zapier was built for a very specific era of the internet. An era where most companies ran fewer tools, workflows were mostly linear, and automation meant connecting one app to another with a simple trigger-action rule. That model worked because the problems were smaller.
But the operating environment has changed. Modern teams don’t just connect apps. They coordinate distributed systems, AI agents, APIs, internal dashboards, customer-facing workflows, and real-time data streams. Automation is no longer glue between tools. It’s becoming the execution layer of the business itself.
That shift fundamentally changes what “automation” needs to do. Trigger-action logic works for notifications and simple data sync. It struggles when workflows become stateful, multi-branch, AI-dependent, or product-embedded. What used to feel flexible starts to feel brittle under scale, complexity, and volume.
At the same time, AI has moved from experiment to infrastructure. Workflows are no longer just “if X, then Y.” They are “if X, evaluate context, retrieve memory, generate output, update state, trigger downstream systems.” That requires orchestration, not just automation.
And when automation becomes infrastructure, pricing models, execution engines, and architectural depth start to matter far more than integration count.
This is why so many teams searching for Zapier alternatives aren’t simply cost-sensitive.
They’re hitting structural ceilings. The industry didn’t abandon trigger-action tools; it evolved beyond them. The question now isn’t whether Zapier works.
The question is whether the model it represents is sufficient for where automation is heading.
What Zapier Actually Is (And What It Isn’t)?
At its core, Zapier is a trigger-action automation engine. You define an event in one application, the trigger, and map it to an action in another. When the trigger fires, the action executes. Over time, Zapier expanded this model to include multi-step workflows, conditional paths, filters, and thousands of integrations.
Its real innovation wasn’t just connectivity. It was accessibility. Zapier abstracted APIs into simple interfaces. It removed the need for custom scripts. It made automation available to non-technical operators. For startups and SMBs trying to stitch together SaaS tools quickly, that was transformative.
Its economic model followed the same philosophy.Pricing is typically based on tasks, meaning each time a workflow runs and performs an action, it counts toward usage. For low-volume workflows, this is predictable and manageable. For small teams running linear automations, it’s often sufficient.
But here’s what Zapier isn’t.
It is not a backend infrastructure layer.
It is not a product development platform.
It is not a stateful orchestration engine.
It is not designed to embed automation deeply into application logic.
Zapier connects tools, but it isn’t the execution core of your system a distinction that matters far more in 2026 than it did in 2016. Trigger-action is powerful when automation is peripheral; once automation becomes central, architecture matters. That’s when the conversation shifts from integrations to infrastructure.
The Automation Maturity Ladder
Most automation discussions fail because they treat all workflows as equal.
They aren’t.
Connecting a form to a spreadsheet is not the same as orchestrating AI agents across a customer-facing product. Syncing CRM contacts is not the same as running stateful decision systems that influence revenue, operations, and user experience in real time.
Automation evolves in layers. And each layer demands a different architectural foundation.
Level 1 — Task Sync Automation
This is the entry point.
A trigger fires. An action executes. A notification is sent. A record is updated. These workflows are typically linear, event-based, and low volume. The business impact is helpful but not foundational. If they fail occasionally, it’s inconvenient, not catastrophic.
Zapier was built for this layer, and it still performs well here.
Level 2 — Logic-Based Workflow Automation
At this stage, workflows become more complex. You introduce branching paths, filters, multi-step sequences, conditional logic, and API chaining. Volume increases. Edge cases multiply. Reliability starts to matter more.
This is where many growing companies live. It’s also where friction begins. The more logic you add, the more fragile traditional trigger-action systems can become, especially when workflows need to account for context, state, and scale.
Tools like n8n and Make extend deeper into this layer by giving developers more control. But they’re still operating primarily within workflow architecture, not system architecture.
Level 3 — AI-Orchestrated Systems
This is where the shift accelerates.
Workflows are no longer simple logic trees. They involve AI inference, contextual reasoning, dynamic decision-making, memory retrieval, and multi-system coordination. Instead of “if X, then Y,” the logic becomes “if X, evaluate context, generate response, update state, trigger downstream processes.”
At this level, automation isn’t just moving data. It’s making decisions.
The execution engine must handle variability, latency, scale, and observability in ways that traditional automation platforms were never designed to support.
Level 4 — Automation as Infrastructure
This is the highest maturity layer.
Automation stops being a supporting tool and becomes part of the company’s operational backbone. It integrates directly into products, internal dashboards, customer journeys, AI agents, and backend services. It is stateful, scalable, and deeply embedded.
At this stage, pricing models, execution architecture, and deployment flexibility matter more than integration count. The system must behave like infrastructure, not like a collection of stitched-together workflows.
Most teams searching for Zapier alternatives aren’t consciously thinking in these levels.
But many of them are already operating at Level 3 problems while using Level 2 tooling and that mismatch is where frustration begins.
Automation maturity isn’t about how many tools you connect, it’s about how deeply automation is embedded into the way your system actually runs.
Why Are Users and Businesses Looking for Zapier Alternatives?
Opaque Pricing and Task Limits Undermine Predictability
User reviews frequently mention confusion around feature gating and task-based billing, especially when essential filters or advanced steps require upgrading after workflows are already built. Failed runs consuming billable tasks further intensify cost unpredictability.
When automation becomes operationally important, unclear pricing mechanics and execution-based billing can erode trust quickly, particularly for teams managing tight budgets or scaling usage rapidly
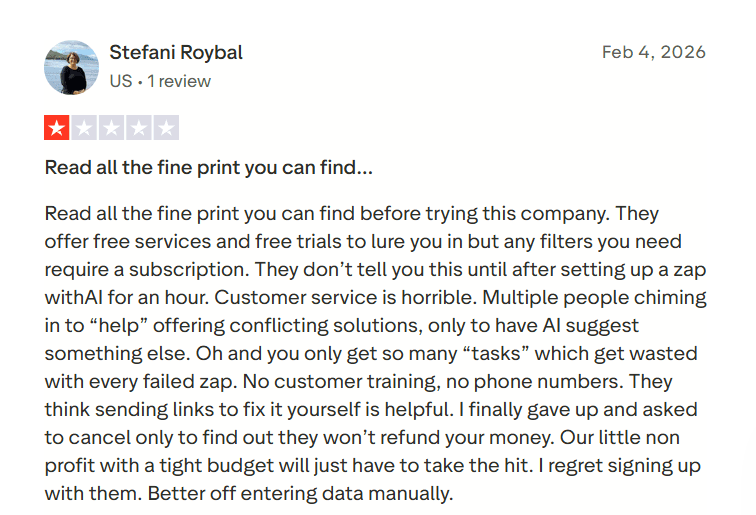
Source: Trustpilot
Workflow Instability and Limited Production Reliability
Some user feedback highlights frustration around platform updates impacting previously stable workflows, requiring repeated workarounds when integrations or internal changes affect execution. For teams relying on automation in production environments, this introduces operational risk.
Concerns are also raised about slow or unclear support escalation for reported bugs, especially when timelines for resolution are not communicated transparently. As automation becomes mission-critical, reliability and accountability matter far more than convenience.
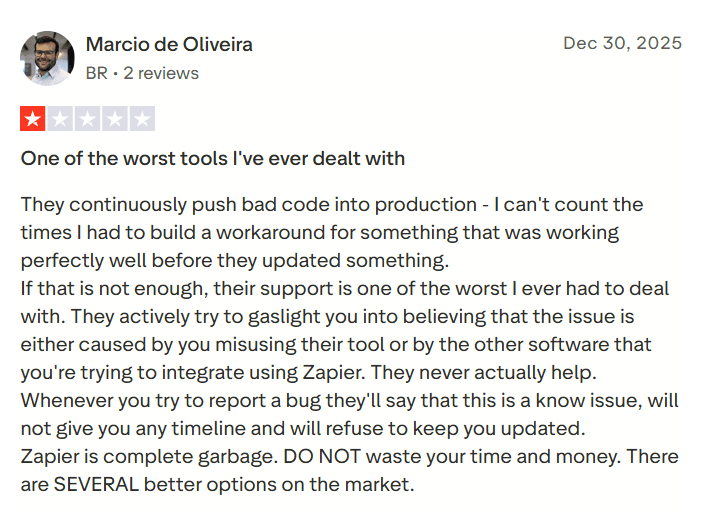
Source: Trustpilot
Task-Based Pricing Scales With Growth, Not Value
Several discussions highlight how task-based billing increases proportionally with business growth, especially in multi-step workflows where each action counts separately. As lead volume or automation depth increases, monthly costs can rise sharply, even for relatively simple operational processes.
A recurring concern is that teams begin optimizing workflows around task limits rather than business efficiency, removing steps or reducing automation depth purely to control billing. When pricing starts shaping system design decisions, the economic model itself becomes a constraint.

Source: Reddit
Escalating Costs and Workflow Breakage at High Volume
Long-term users report significant cost increases as automation volume scales, particularly when moving from small starter workflows to high-frequency execution environments. What begins as affordable entry pricing can become materially expensive at millions of runs per month.
There are also concerns around workflow stability under heavier loads, with users questioning reliability when automations become central to operations. At scale, teams evaluate not just integrations and ease of use, but performance consistency and cost sustainability.
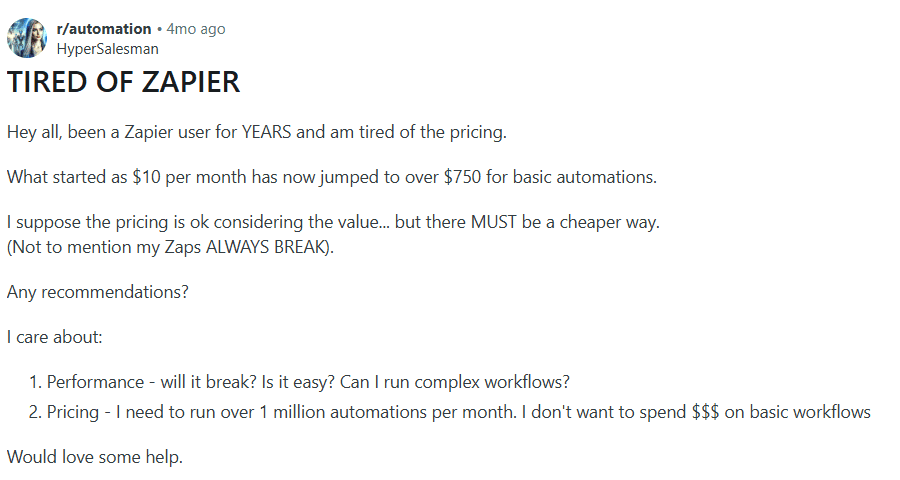
Source: Reddit
Connector-Level Failures Can Disrupt Revenue-Critical Workflows
Some users report automation breakdowns triggered by mapping or connector errors, resulting in stalled workflows and delayed lead processing. When outbound sequences or revenue pipelines depend on uninterrupted execution, even short disruptions can have compounding impact.
As automation becomes embedded in growth and customer acquisition systems, teams increasingly prioritize native orchestration and deeper system integration over surface-level connectors that may introduce single points of failure.

Source: Reddit
What a True Zapier Replacement Should Offer in 2026?
If teams are running into cost ceilings, reliability issues, connector fragility, and workflow constraints, the solution is not just a “cheaper Zapier.”
It’s a different architectural model.
A true replacement in 2026 needs to go beyond task automation and address the structural limitations exposed at scale. That means rethinking how workflows are executed, how pricing scales, and how deeply automation integrates into core systems.
Execution That Scales Without Punishing Growth
Automation pricing should not increase linearly with every additional step or successful customer interaction. When workflow volume grows, costs should reflect infrastructure efficiency, not event taxation. Sustainable execution models allow teams to scale operations without redesigning flows purely to reduce billing exposure.
Stateful and Logic-Heavy Orchestration
Modern workflows are not linear. They branch, evaluate context, reference past interactions, and coordinate across multiple systems. A viable replacement must handle conditional depth, looping logic, and multi-system orchestration without becoming brittle or overly complex to maintain.
AI-Native Workflow Architecture
AI should not be an add-on step in a linear flow. It should be embedded into the execution layer itself. Whether generating content, evaluating lead quality, or orchestrating decision trees, AI-native systems treat intelligence as core infrastructure rather than an optional extension.
Observability and Production Reliability
As automation moves into revenue, operations, and product systems, visibility becomes essential. Teams need transparency into failures, performance bottlenecks, and execution states. Reliable platforms provide monitoring, debugging clarity, and predictable behavior under load.
Product-Level Integration, Not Just App Connectivity
The next generation of automation is embedded directly into products, dashboards, internal tools, and customer experiences. That requires more than connectors. It requires infrastructure-level integration, authentication handling, deployment flexibility, and system-level control.
The 7 Best Zapier Alternatives Ranked by Automation Depth
Not all Zapier alternatives solve the same problem.
Some offer cheaper task execution.
Some offer more flexible workflow control.
Some extend into enterprise governance.
And a small subset rethink automation at the infrastructure level.
Ranking by popularity or feature count hides that distinction. So instead, we’re ranking these platforms by automation depth, meaning how far you can scale before architectural limits begin to appear.
Level 4 — Automation as Infrastructure
Emergent — AI-Native Infrastructure Automation
Designed for teams building automation into products, AI systems, and backend architecture. Operates beyond trigger-action workflows and into execution-layer orchestration.
Level 3 — Enterprise Orchestration Platforms
Workato — Enterprise Integration Automation
Strong governance, enterprise integrations, and compliance tooling. Built for larger organizations integrating internal systems at scale.
Tray.io — Enterprise Workflow Orchestration
Advanced workflow tooling with enterprise positioning, offering deeper control than traditional no-code automation platforms.
Level 2.5 — Developer-Centric Workflow Engines
n8n — Developer-Controlled Workflow Automation
Open-core and API-flexible, giving technical teams more control over logic and hosting environments.
Level 2 — Advanced Logic-Based Automation
Make — Visual Multi-Step Workflow Builder
Powerful branching logic and visual orchestration, but still rooted in event-driven execution.
Activepieces — Modular Open-Source Automation
Community-driven automation with flexibility and self-hosting options, focused primarily on workflow construction.
Pabbly Connect — Budget Trigger-Action Automation
Lower-cost alternative for basic linear automations with limited architectural depth.
Why this ranking matters:
If you are automating a handful of notifications, most Level 2 tools are sufficient.
If you are orchestrating AI workflows, embedding automation into products, or running high-volume execution environments, only Level 4 platforms operate at the necessary depth.
The question is not which tool is cheaper.
The question is which layer your system actually belongs to.
The 7 Best Zapier Alternatives Ranked by Automation Depth
Emergent — Level 4 Automation Infrastructure
Who It’s Built For?
Emergent is built for teams operating at Level 4 on the automation maturity ladder, where workflows are no longer peripheral glue but core execution infrastructure. This includes AI-first startups embedding logic into their products, growth teams orchestrating stateful pipelines, and technical operators who treat automation as backend architecture rather than as task sequencing.
If automation directly influences revenue, product behavior, or operational systems, you’re already beyond simple trigger-action territory. That’s the layer Emergent is designed to serve.
Architectural Advantage
At Level 4, automation must behave like infrastructure.
Emergent’s execution model is built around AI-native orchestration, state awareness, and system-level integration. Instead of counting isolated task executions, it focuses on scalable execution environments where workflows can grow in depth and intelligence without forcing economic compromises.
This allows teams to design automation around business logic and AI reasoning, not around step minimization or billing avoidance.
Where It Wins Over Zapier?
Zapier connects applications efficiently at workflow level. Emergent operates one layer deeper, where automation is embedded into systems themselves.
When workflows require AI decision-making, persistent state, backend integration, or product-level deployment, the architectural difference becomes visible. Rather than stitching together steps, teams can design coordinated systems that behave predictably under scale.
That distinction matters most when automation stops being a convenience and starts being core infrastructure.
When It’s Not the Right Fit?
If your use case is limited to low-volume, linear task automation between a few SaaS tools, Level 2 platforms like Zapier may be more than sufficient.
Emergent is designed for complexity, scale, and system depth. For simple notification workflows or small internal automations, its capabilities may exceed what you actually need.
n8n — Developer-Controlled Workflows
Who It’s Best For?
n8n is best suited for technical teams that want more control than traditional no-code automation platforms provide. It appeals to developers who prefer API-level access, custom logic handling, and the flexibility of self-hosting, particularly in environments where data ownership and customization matter.
Teams operating at Level 2 to 2.5 on the automation maturity ladder, where workflows are logic-heavy but not yet full infrastructure, will find n8n significantly more adaptable than simple trigger-action tools.
Where It Improves on Zapier?
Compared to Zapier, n8n offers deeper control over workflow logic and execution. Its node-based structure allows more complex branching, custom scripting, and integration handling without being tightly constrained by rigid task abstractions.
For developers who find Zapier limiting in terms of flexibility or customization, n8n provides a more extensible workflow engine that better supports API-driven automation.
Where It Still Hits a Ceiling?
Despite its flexibility, n8n remains primarily a workflow orchestration platform rather than a full automation infrastructure layer. While it enables complex logic and hosting control, it does not inherently provide AI-native orchestration, product-level embedding, or execution models designed for infrastructure-scale automation.
For teams moving toward Level 3 and Level 4 systems, additional architectural components are typically required beyond what n8n alone offers.
Make — Visual Automation Platform
Who It’s Best For?
Make is ideal for operators and power users who want advanced branching logic within a visual workflow builder. It appeals to teams that need more flexibility than Zapier offers but still prefer a structured, visual interface over code-centric control.
Companies operating at Level 2 automation maturity, where workflows are multi-step and logic-driven but not yet infrastructure-level, will find Make well aligned with their needs.
Where It Improves on Zapier?
Make provides more granular control over multi-step workflows and conditional logic compared to traditional trigger-action setups. Its visual scenario builder allows users to map complex sequences with clearer visibility into branching paths and data transformation.
For teams outgrowing linear Zaps but not yet requiring full system orchestration, Make offers a noticeable step up in workflow depth.
Where It Still Hits a Ceiling?
Despite its flexibility, Make remains rooted in event-driven workflow execution. AI capabilities and infrastructure-level orchestration are not native architectural primitives, and execution still revolves around operation-based billing.
As workflows grow more stateful or become deeply embedded into products, teams may encounter limitations in scalability and system-level integration depth.
Workato — Enterprise Automation
Who It’s Best For?
Workato is built for mid-sized to large enterprises that require structured governance, compliance controls, and cross-departmental system integration. It is particularly suited for organizations managing ERP, CRM, HR, and finance platforms at scale, where automation intersects with security and regulatory requirements.
Teams operating at Level 3 automation maturity, where orchestration spans multiple internal systems and reliability is mission-critical, will find Workato aligned with enterprise-grade expectations.
Where It Improves on Zapier?
Compared to Zapier, Workato offers stronger enterprise controls, advanced integration depth, and built-in governance capabilities. It is designed to handle complex, multi-system automation across departments rather than lightweight app-to-app workflows.
For larger organizations that require centralized visibility, role-based access, and compliance-ready automation frameworks, Workato provides a more structured operational layer.
Where It Still Hits a Ceiling?
Despite its enterprise strength, Workato remains primarily an integration and orchestration platform rather than an AI-native infrastructure system. Automation is still workflow-centric, and embedding deeply intelligent, state-aware execution into products typically requires additional architectural layers.
For teams moving toward AI-first, product-embedded automation at Level 4 maturity, Workato can serve as an integration backbone but not necessarily the execution core.
Activepieces — Open Source Workflow Builder
Who It’s Best For?
Activepieces is best suited for teams that prefer open-source flexibility and greater control over deployment environments. It appeals to startups and technical operators who want workflow automation without being locked into proprietary ecosystems.
Teams operating at Level 2 automation maturity, where workflows are structured but not deeply embedded into product infrastructure, will find Activepieces a practical and customizable option.
Where It Improves on Zapier?
Compared to Zapier, Activepieces offers open-source transparency and the ability to self-host, giving teams more ownership over their automation environment. This can reduce dependency on third-party pricing shifts and provide greater customization at the workflow level.
For teams concerned about vendor lock-in or looking for lighter-weight automation control, it presents a more flexible alternative.
Where It Still Hits a Ceiling?
Despite its openness, Activepieces remains primarily a workflow automation tool. Its architecture centers on event-driven sequences rather than infrastructure-level orchestration, and advanced AI-native execution is not a core primitive.
As automation needs evolve toward stateful systems or product-embedded intelligence, additional infrastructure layers are typically required beyond what Activepieces alone provides.
Tray.io — Enterprise Workflow Orchestration
Who It’s Best For?
Tray.io is designed for enterprises that require structured, scalable workflow automation across multiple internal and external systems. It appeals to organizations that need deeper integration layers than basic no-code tools provide, particularly in sales, marketing, and operations environments.
Teams operating at Level 3 automation maturity, where orchestration spans departments and systems, will find Tray.io aligned with enterprise workflow needs.
Where It Improves on Zapier?
Compared to Zapier, Tray.io provides more advanced workflow control, stronger integration depth, and better support for enterprise-scale automation. Its architecture supports more complex branching, API interactions, and multi-system coordination than traditional trigger-action tools.
For companies that have outgrown simple linear workflows, Tray.io offers a more robust orchestration layer.
Where It Still Hits a Ceiling?
Despite its enterprise orientation, Tray.io remains primarily workflow-centric rather than infrastructure-native. Automation is structured around orchestration between systems rather than embedding execution directly into products or AI-native environments.
For teams progressing toward Level 4 automation maturity, Tray.io may function as a strong integration layer but not the foundational execution core.
Pabbly Connect — Budget Trigger-Action Automation
Who It’s Best For?
Pabbly Connect is best suited for small teams and solopreneurs looking for a lower-cost alternative to traditional task-based automation platforms. It appeals to users who need simple app-to-app workflows without advanced logic, enterprise controls, or AI orchestration.
Teams operating at Level 1 or early Level 2 automation maturity, where workflows are linear and volume is moderate, will find it sufficient for basic operational needs.
Where It Improves on Zapier?
Compared to Zapier, Pabbly Connect often positions itself as a more affordable option for similar trigger-action use cases. For users primarily concerned with reducing subscription costs while maintaining basic automation capabilities, it can serve as a practical substitute.
It addresses entry-level automation needs without the pricing structure that some users find restrictive at scale.
Where It Still Hits a Ceiling?
Pabbly Connect remains fundamentally rooted in the same trigger-action paradigm as Zapier. It does not materially extend automation into AI-native orchestration, infrastructure-level execution, or deeply embedded product systems.
As workflows grow in complexity, statefulness, or strategic importance, its architectural depth remains limited to task automation rather than system orchestration.
Cost Curve Comparison: Task-Based vs Infrastructure Automation
As automation becomes central to operations, pricing models begin to influence architecture decisions. The difference between task-metered workflows and infrastructure-level execution becomes more visible at scale.
Here’s how the two models compare:
Dimension | Task-Based Automation (e.g., traditional trigger-action tools) | Infrastructure-Level Automation (Level 4 systems) |
Billing Unit | Charged per task, action, or operation executed | Charged based on execution environment or infrastructure usage |
Cost Growth Pattern | Scales linearly or exponentially with workflow volume | Scales with system resources, not individual task count |
Impact of Multi-Step Workflows | Each additional step increases billable events | Workflow complexity does not automatically multiply cost |
Effect of Failed Runs | Failed or retried executions may still consume billable tasks | Cost tied to execution environment, not isolated failures |
Behavioral Incentive | Encourages minimizing steps to control billing | Encourages optimizing logic for performance and outcomes |
Scalability Under High Volume | Can become expensive at large execution counts | Designed to handle higher volume without event-based penalty |
Architecture Mindset | Automation as a utility layer | Automation as operational infrastructure |
The core difference is not price at entry level.
At low volume, task-based tools are often affordable and convenient.
The divergence appears when automation moves from peripheral tasks to revenue systems, AI workflows, or product logic. At that point, execution economics start shaping design decisions. Teams either optimize for business outcomes, or they optimize for task reduction.
The pricing model quietly influences the architecture and architecture determines long-term scalability.
Who Should NOT Leave Zapier?
Despite the structural ceilings discussed above, Zapier remains a strong fit for many teams. Not every organization needs infrastructure-level automation, and forcing complexity where it isn’t required can introduce unnecessary overhead.
You likely should stay with Zapier if:
You run low-volume, linear automations between a handful of SaaS tools, and those workflows are stable and predictable.
Your automation use cases are primarily notifications, simple data sync, or lightweight operational tasks.
You do not require AI-native orchestration, stateful logic, or deep backend embedding into your product.
Your monthly task volume is manageable and cost growth has not materially affected your operating margin.
For these scenarios, Zapier continues to offer ease of use, wide integration coverage, and quick setup without architectural complexity.
The decision to move away from Zapier is not about trend adoption. It’s about system maturity.
If automation is still peripheral to your operations, staying with a Level 2 platform can be entirely rational.If automation is becoming foundational, that’s when the conversation changes.
Migration Blueprint: Moving Beyond Zapier Without Breaking Workflows
Moving away from Zapier should not feel like ripping out a live system. The goal is controlled transition, not disruption.
Here’s a structured migration path:
Step | Action | Why It Matters | Outcome |
1. Audit All Active Zaps | Document every workflow, trigger source, action depth, and monthly task volume | Identifies high-impact automations and hidden cost drivers | Clear visibility into operational dependency |
2. Classify by Maturity Level | Tag each workflow as Level 1, 2, or 3 based on complexity and business impact | Separates simple automations from system-critical flows | Prioritization clarity |
3. Identify Cost-Heavy or Logic-Heavy Flows | Isolate workflows with high task counts or multi-step branching | These are typically first to hit pricing or structural ceilings | High-leverage migration targets |
4. Rebuild Critical Workflows in Parallel | Recreate priority automations in the new environment before disabling Zaps | Prevents downtime and reduces operational risk | Seamless transition |
5. Monitor Performance and Execution Stability | Track latency, failure rates, and execution behavior post-migration | Ensures system-level reliability before full switchover | Confident rollout |
6. Sunset Redundant or Overlapping Automations | Remove legacy workflows once replacements are verified | Eliminates cost leakage and duplication | Leaner automation architecture |
The key is not replacing everything at once.
Most teams discover that only a subset of workflows actually require deeper architectural capability. Those are the ones driving cost, complexity, or reliability concerns.
Start there.
Migration is not about abandoning what works.
It’s about aligning your automation stack with your actual maturity level.
Why Emergent Is the Most Future-Proof Zapier Alternative?
Automation Is Moving From Workflows to Infrastructure
The automation landscape is shifting from linear trigger-action flows to system-level orchestration embedded directly into products, operations, and AI execution layers. Platforms built only for app connectivity struggle when workflows become stateful, multi-system, and revenue-critical.
Emergent is positioned at this infrastructure layer, where automation behaves like backend architecture rather than a sequence of isolated tasks. That structural alignment is what makes it resilient as systems grow in complexity.
Task-Based Pricing Breaks at Scale
Per-task billing models work well at low volume but scale mechanically with growth, forcing teams to simplify logic or limit execution to manage cost exposure. Over time, pricing begins influencing architecture decisions instead of business logic driving design.
Emergent’s execution model is aligned with infrastructure economics rather than event taxation, allowing workflows to grow in depth and intelligence without penalizing every additional step. This decoupling of cost from step count becomes critical at higher automation maturity levels.
AI Must Be Native, Not Bolted On
As AI becomes embedded into workflows, it can no longer function as a single action inside a linear chain. AI-native systems require orchestration layers that understand context, manage state, and coordinate multiple downstream systems dynamically.
Emergent treats AI as a foundational execution primitive rather than an optional extension, enabling decision-making, reasoning, and multi-system coordination to operate cohesively within the automation environment.
System-Level Control Outlasts App Connectivity
Connecting SaaS tools solves immediate operational gaps, but long-term scalability depends on deeper integration into backend systems, authentication layers, and product logic. Platforms that remain at the connector level often require additional tooling as automation becomes core infrastructure.
Emergent is designed to embed automation directly into system architecture, supporting backend integration, deployment flexibility, and product-level execution without forcing teams to re-platform as complexity increases.
Level 4 Automation Maturity Is the Strategic Endgame
Teams rarely plan to outgrow their automation stack, but as workflows evolve into revenue pipelines, AI agents, and operational backbones, architectural ceilings become visible. Tools built for workflow convenience often require replacement when automation becomes strategic.
Emergent is aligned with Level 4 automation maturity from the outset, enabling organizations to scale from internal workflows to infrastructure-level orchestration without redesigning their core execution environment.
Final Verdict
Zapier remains one of the most recognizable names in automation, and for simple, linear workflows it continues to serve its purpose effectively. But automation in 2026 is no longer defined by app connectivity alone. As systems become AI-driven, state-aware, and operationally central, the underlying architecture begins to matter far more than integration count or entry-level convenience.
The real decision is not which tool is cheaper. It is which platform matches your automation maturity. If you are operating at Level 1 or Level 2, traditional workflow tools may be sufficient. If you are building AI-native systems, scaling execution-heavy environments, or embedding automation into your product infrastructure, platforms designed for Level 4 maturity, like Emergent, align more closely with where the industry is heading.


