Alternatives and Competitors
•
Jan 21, 2026
5 Best Adalo Alternatives and Competitors in 2026
Look at the best Adalo alternatives in 2026. Compare Emergent, FlutterFlow, Thunkable, Draftbit & Budibase for scalability and long-term app growth.
Written By :

Devansh Bansal
No-code app builders have made it easier than ever to turn ideas into functional mobile and web applications without traditional development teams. Platforms like Adalo helped popularize this shift by giving non-technical users a visual way to design apps and publish them quickly. As adoption has grown, expectations have changed. Teams now want more than just speed. They want apps that can handle real users, real data, and real business logic without constant workarounds or rebuilds. This shift has pushed the no-code space toward platforms that balance accessibility with long-term flexibility.
For many Adalo users, the decision to look for alternatives comes after initial success. What starts as a simple MVP often grows into something more serious, exposing limits around performance, data handling, integrations, and scalability. Choosing the right Adalo alternative matters because switching platforms later is costly and disruptive. This guide is designed to help you evaluate credible competitors based on how far they can grow with your app. Rather than listing features, it focuses on how each platform fits different stages of product maturity and team capability.
Challenges with Adalo and Why Existing Users Are Looking for Alternatives
Scalability Issues for Growing User Bases
Verified users report that Adalo performs poorly once your app exceeds basic usage levels, especially as the number of users grows.
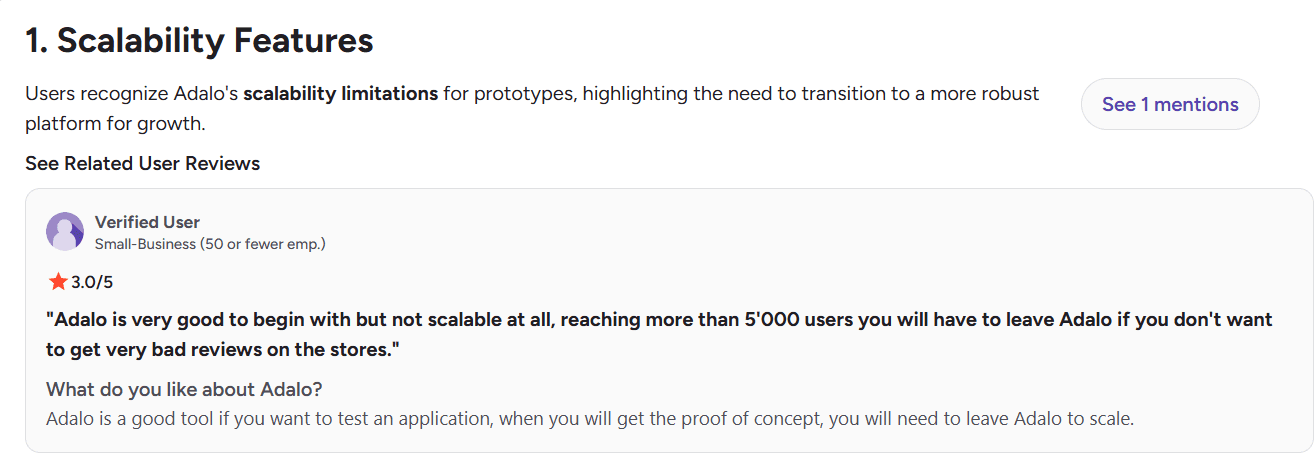
Source: G2
Perception of Unresponsive Product Direction and Frustration
Some users express frustration with Adalo’s development pace and ongoing product direction. In community discussions, users have critiqued Adalo for not addressing core problems and for changes in pricing or feature rollout that left long-time builders dissatisfied.

Source: Reddit
Account and Billing Friction
Real user discussions include complaints about billing behavior, where a user reported that their account was charged repeatedly even after cancellation. Issues around billing transparency and control can erode trust, especially for small teams or startups managing tight budgets.

Source: Reddit
Best Adalo Alternatives for No-Code App Builders in 2026
5 Best Adalo Alternatives You Should Know About:
Emergent
Emergent is one of the best, full-stack, AI-powered vibe coding and no code platforms for building web and mobile applications. Instead of assembling apps screen by screen, Emergent lets teams describe what they want in natural language and turns that into working software. It generates frontend, backend, logic, and deployment together inside a single workflow. Unlike Adalo’s UI-driven approach, Emergent treats the app as a complete system from day one. This removes many of the structural limits that appear as apps grow. Teams typically choose Emergent when they want speed without locking themselves into early shortcuts. It is positioned for long-term product ownership rather than quick MVPs only.
Key Features of Emergent
Natural language app building
Emergent allows users to define app behavior in plain English instead of wiring actions to UI elements. The system converts intent into structured application logic. This reduces the cognitive load of managing complex flows. Adalo users often find this easier once apps move beyond simple interactions. Changes happen through conversation, not rewiring screens.
Full-stack generation by default
Frontend, backend services, data handling, and authentication are created together. There is no need to patch multiple tools to get a working product. Adalo users typically manage logic and UI tightly together. Emergent separates concerns cleanly from the start, which supports growth.
Production-ready architecture
Apps are structured to scale without major rework. Data, logic, and interface are not tightly coupled. This prevents fragility as features are added. Teams avoid the “rebuild later” problem common with UI-first builders.
Built-in testing and iteration
Emergent supports testing as part of the build loop. Teams can validate behavior before updates go live. This reduces surprises once real users are active. Adalo users often rely on manual testing at this stage.
End-to-end deployment
Deployment happens inside the platform without external setup. Hosting, updates, and revisions are handled in one place. This keeps ownership centralized and reduces operational friction as the app evolves.
Who Should Use Emergent?
Founders building serious products
Emergent fits teams moving beyond early MVPs. It supports growth without forcing architectural compromises. This reduces long-term migration risk.
Teams outgrowing UI-first builders
Users frustrated by logic spread across screens often prefer Emergent’s system-first approach. It simplifies complexity. This makes scaling behavior easier to manage.
Businesses with complex workflows
Multi-step processes and internal logic live inside the app itself. This reduces dependency on external tools. Reliability improves as workflows grow.
Teams thinking in systems, not layouts
Emergent works best when teams focus on outcomes rather than just UI design. It rewards clarity of intent. This suits mature product teams.
Advantages vs Limitations
Advantages | Limitations |
Full-stack apps without UI-logic coupling | More capability than very simple apps require |
Natural language build and iteration | Requires clear thinking to guide outcomes |
Designed for production use | Less suited for throwaway prototypes |
Scales without major restructuring | |
Built-in testing and deployment | |
Long-term ownership and flexibility |
Pricing
Plan | Pricing | Key Highlights |
Free | $0/month |
|
Standard | $20/month |
|
Pro | $200/month |
|
Team | $300/month |
|
Read More About: Emergent Pricing and Plans
Flutterflow
Flutterflow is a low-code app builder built on top of Google’s Flutter framework, designed for teams that want visual development with real, exportable code underneath. Apps created in Flutterflow compile into native mobile and web applications rather than runtime wrappers. Unlike Adalo’s UI-first, action-based logic, Flutterflow exposes app structure, state, and navigation more explicitly. This gives builders more control over how apps behave as complexity increases. The platform is commonly chosen when performance, scalability, and code ownership start to matter. Flutterflow sits between pure no-code tools and full custom development. It is positioned for teams building serious mobile products without starting from scratch.
Key Features of Flutterflow
Visual builder backed by Flutter code
Flutterflow lets users design screens visually while generating real Flutter code in the background. This provides transparency into how the app is structured. Adalo users gain more control over layout and behavior. The trade-off is a steeper learning curve.
Native mobile and web output
Apps compile into native iOS, Android, and web builds. Performance is closer to custom development than most no-code tools. This matters once apps have real users. Flutterflow is often chosen when Adalo apps begin to feel slow.
Advanced state and navigation control
Flutterflow exposes app state, routing, and conditional flows clearly. This supports complex user journeys and interactions. Adalo users often struggle here as logic grows. Flutterflow handles this more cleanly.
Backend and API integration
The platform supports REST APIs, Firebase, and external backends. This allows apps to connect real services without heavy workarounds. Compared to Adalo, integrations feel more native. It supports production use cases better.
Code export and ownership
Users can export their Flutter code and continue development outside the platform. This reduces vendor lock-in. For long-term products, this is a major advantage. Adalo does not offer this flexibility.
Who Should Use Flutterflow?
Teams building performance-critical apps
Flutterflow suits apps where speed and responsiveness matter. Native output delivers better performance. This is important for consumer apps. Teams often switch from Adalo for this reason.
Founders comfortable with technical concepts
While no coding is required, understanding state and APIs helps. Builders willing to learn get more control. Flutterflow rewards effort. It is less forgiving than simpler tools.
Startups planning long-term ownership
Code export reduces future risk. Teams can transition to custom development if needed. This aligns with long-term roadmaps. Flutterflow supports growth.
Hybrid design and engineering teams
Flutterflow works well when designers and developers collaborate. Visual design and code coexist. This flexibility is uncommon in pure no-code tools.
Advantages vs Limitations
Advantages | Limitations |
Native mobile and web performance | Steeper learning curve than Adalo |
Visual building with real code output | More configuration required upfront |
Strong backend and API support | UI building takes longer |
Code export reduces lock-in | Debugging can feel technical |
Suitable for complex app logic | Not ideal for very fast prototypes |
Scales better than UI-first builders | Requires comfort with app structure |
Pricing
Plans | Pricing | Key Highlights |
Free | $0 per month |
|
Basic | $39 per month |
|
Growth | $80 per month for first seat, $55 for additional seats |
|
Business | $60 per month for first seat, $41.25 for seats 2–5 |
|
Thunkable
Thunkable is a no-code mobile app builder built around visual block-based programming. It allows users to create native mobile apps for iOS and Android by connecting logic blocks to UI components. Compared to Adalo’s action-based flows, Thunkable gives more explicit control over logic through blocks. This makes it powerful for certain interactions, but also harder to manage as apps grow. Thunkable is often chosen by users who want more control than simple UI builders without writing code. It works best for small to mid-sized mobile apps with defined behavior. The platform is positioned as a learning-friendly and logic-focused builder rather than a long-term product platform.
Key Features of Thunkable
Block-based visual logic system
Thunkable uses drag-and-drop blocks to define app behavior. This makes logic visible and explicit. Adalo users often appreciate the clarity for simple workflows. As logic grows, blocks can become harder to manage.
Native mobile app output
Apps are compiled into native iOS and Android builds. This avoids web wrappers and improves performance. It suits mobile-first use cases. Web support is limited compared to other platforms.
Built-in components and sensors
Thunkable includes access to device features like camera, GPS, and sensors. This supports interactive mobile experiences. Adalo users sometimes lack this depth. It is a strong point for hardware-driven apps.
API and data integrations
The platform supports REST APIs and external data sources. This allows apps to connect to real services. Integrations work well for basic use cases. Complex workflows require careful block management.
Live testing during development
Thunkable allows live previews on devices during development. This speeds up iteration. Immediate feedback helps beginners. It becomes less effective as projects scale.
Who Should Use Thunkable?
Builders focused on mobile-first apps
Thunkable is suited for teams targeting native mobile experiences. It handles device features well. Web-first products are a weaker fit.
Users comfortable with visual logic
Teams that think in flows and conditions benefit from block-based logic. It offers more control than simple UI builders. It requires patience as complexity increases.
Educational and learning-driven projects
Thunkable is popular in learning environments. It helps users understand app logic visually. This makes it accessible for beginners. Long-term scaling is secondary.
Small teams with defined app scope
Apps with clear boundaries and limited growth plans work well. As scope expands, friction increases. Planning ahead is important.
Advantages vs Limitations
Advantages | Limitations |
Clear, visual logic through blocks | Logic becomes hard to manage at scale |
Native mobile app performance | Limited support for complex products |
Strong access to device features | Web app capabilities are basic |
Live testing during development | Performance issues as projects grow |
More logic control than UI-first tools | Not ideal for long-term scalability |
Good for learning app behavior | UI control is less flexible |
Pricing
Plans | Pricing | Key Highlights |
Free | $0 per month |
|
Accelerator | $19 per month |
|
Builder | $59 per month |
|
Advanced | $189 per month |
|
Education | Custom |
|
Draftbit
Draftbit is a low-code app builder designed for teams that want visual development without giving up code-level control. It is built on React Native, which means apps are generated as real, exportable code rather than locked into a runtime. Unlike Adalo’s UI-first abstraction, Draftbit exposes app structure, navigation, and logic more directly. This makes it more flexible, but also more demanding to use. Teams often choose Draftbit when they want to collaborate visually and still own the final codebase. It is positioned as a bridge between no-code speed and traditional development workflows. Draftbit fits teams building production mobile apps with long-term ownership in mind.
Key Features of Draftbit
Visual builder with React Native code
Draftbit lets users design screens visually while generating React Native code underneath. This keeps development transparent. Adalo users gain more control over layout and behavior. The trade-off is a higher learning curve.
Full code export and GitHub workflow
Apps can be exported and maintained outside the platform. Teams can move into a standard GitHub-based workflow. This reduces vendor lock-in. It suits long-term product roadmaps.
Flexible navigation and state management
Draftbit exposes navigation stacks and state clearly. This supports complex app flows. Adalo users often struggle with this as logic grows. Draftbit handles it more cleanly.
Backend and API integrations
The platform connects easily to REST APIs and common backend services. This enables real-world data handling. Compared to Adalo, integrations feel less constrained. It supports production use cases better.
Collaboration-friendly development
Draftbit supports team workflows where designers and developers work together. Visual changes and code coexist. This flexibility is valuable in mixed-skill teams.
Who Should Use Draftbit?
Teams planning long-term app ownership
Draftbit suits teams that want to keep control of their code. Exporting reduces future platform risk. This aligns with serious product development.
Founders comfortable with technical concepts
Users do not need to code everything, but technical comfort helps. Understanding components and APIs is useful. Draftbit rewards hands-on involvement.
Mobile-first product teams
Draftbit is well suited for native mobile apps. Performance is strong. Web support is secondary. It fits consumer-facing products.
Hybrid design and engineering teams
Teams where designers and developers collaborate benefit most. Visual tools speed up work. Code access keeps flexibility high.
Advantages vs Limitations
Advantages | Limitations |
Real React Native code output | Steeper learning curve than Adalo |
Full code export and ownership | Requires technical understanding |
Strong API and backend integration | Setup takes longer than simple builders |
Suitable for production mobile apps | Web apps are not the main focus |
Reduces long-term platform lock-in | Debugging can feel developer-oriented |
Good for mixed-skill teams | Not ideal for quick MVPs |
Pricing
Plans | Pricing | Key Highlights |
Free | $0 per month |
|
Standard | $25 per month |
|
Pro | $50 per month |
|
Team | $250 per month |
|
Budibase
Budibase is an open-source low-code platform focused on building internal tools and business applications. It allows teams to create apps on top of databases, APIs, and spreadsheets with a strong emphasis on self-hosting and control. Unlike Adalo, which is optimized for consumer-facing mobile apps, Budibase is designed primarily for internal workflows and admin tools. Apps are built around data models and forms rather than screens and interactions. This makes Budibase more structured, but also less design-flexible. Teams usually choose Budibase when data control, security, and internal efficiency matter more than polished UI. It is positioned as an internal tooling platform rather than a mobile product builder.
Key Features of Budibase
Open-source and self-hosted deployment
Budibase can be self-hosted, giving teams full control over data and infrastructure. This is a major shift from Adalo’s fully managed model. It suits organizations with compliance or data residency needs. The trade-off is more setup responsibility.
Data-first internal app building
Apps are built around data sources like PostgreSQL, MySQL, REST APIs, and spreadsheets. Forms, tables, and workflows are generated from these sources. Adalo users will find this more structured but less visual. It works best for internal operations.
Built-in automation and workflows
Budibase includes native automation for approvals, triggers, and actions. This reduces reliance on third-party tools. For internal processes, this keeps systems simpler. Consumer-style interactions are limited.
Role-based access and permissions
The platform supports granular user roles and permissions. This is critical for internal apps used by multiple teams. Adalo’s access control is more basic by comparison. Budibase prioritizes security over flexibility.
Custom components and extensibility
Developers can extend Budibase with custom components. This adds flexibility where needed. It requires technical involvement. This balance suits teams with mixed skill sets.
Who Should Use Budibase?
Teams building internal business tools
Budibase is well suited for admin panels, dashboards, and internal workflows. These apps prioritize data handling over UI polish. Adalo users building internal tools often switch here.
Organizations with data control requirements
Companies with strict security or compliance needs benefit from self-hosting. Data stays under their control. This is not Adalo’s strength.
Technical teams supporting non-technical users
Budibase works well when developers set up the system and others build on top. It balances accessibility and control. This suits internal platforms.
Businesses not focused on consumer mobile apps
Budibase is not optimized for app store distribution. Web-based internal apps are the main use case. Teams building public mobile apps should look elsewhere.
Advantages vs Limitations
Advantages | Limitations |
Open-source and self-hostable | Not designed for consumer-facing apps |
Strong data control and security | UI customization is limited |
Built-in automation for internal workflows | Requires setup and maintenance |
Flexible role-based permissions | Mobile-first use cases are weak |
Good fit for internal tools | Less suitable for rapid MVPs |
Extensible for technical teams | Some features require technical input |
Pricing(Self Host)
Plans | Pricing | Key Highlights |
Open Source | $0 |
|
Enterprise | Custom |
|
Pricing(Cloud)
Plans | Pricing | Key Highlights |
Pro | $12 per app creator per month + $2.40 per app user per month |
|
Premium | $60 per app creator per month + $6 per app user per month |
|
Enterprise | Custom |
|
How to Choose the Right Adalo Alternative?
Decide Whether You Are Building an MVP or a Long-Term Product
If your goal is to validate an idea quickly, lightweight builders may still work. But if your app is expected to grow into a real product with users, data, and workflows, early shortcuts become liabilities. Adalo alternatives differ sharply in how far they can scale. Choosing with the end state in mind avoids forced rewrites later.
Match the Platform to Your Logic and Workflow Needs
Some platforms handle simple interactions well but struggle with multi-step workflows and complex conditions. If your app relies on automation, integrations, or backend-heavy logic, UI-first tools will hit limits fast. Platforms like Emergent, Flutterflow, or Bubble handle this depth better. Understanding your logic needs upfront narrows choices quickly.
Evaluate Mobile vs Web Priorities
Adalo is mobile-focused, but not all alternatives are. Flutterflow and Draftbit lean heavily into native mobile performance, while Bubble and Budibase are more web-first. If app store distribution and mobile UX are critical, this distinction matters. Platform orientation should align with how users will access your product.
Consider Team Skill Level and Learning Curve
More powerful platforms usually demand more learning. Teams comfortable with technical concepts can unlock far more flexibility. Less technical teams may prefer structured tools with guardrails. The right choice stretches your team without overwhelming it.
Think About Ownership and Future Flexibility
Some platforms allow code export or self-hosting, while others keep you inside their ecosystem. If long-term ownership, customization, or compliance matters, this becomes a deciding factor. Speed is valuable, but lock-in costs often appear later.
Conclusion
Adalo remains a strong choice for quickly launching design-led mobile apps, but many teams outgrow it as products mature. The alternatives covered here represent different paths forward, from production-grade full-stack platforms to internal tooling systems and code-export workflows. There is no single best replacement, only better alignment with how complex your app needs to become. Teams planning for scale, control, and longevity should prioritize architecture over convenience. Choosing the right Adalo alternative is ultimately about removing future constraints, not just solving today’s problems.



